Why HearBright Hearing Aids Work: Reason #2: The Journey
By Nobuko Ito, Au.D. Audiologist HearBright This is the story of a

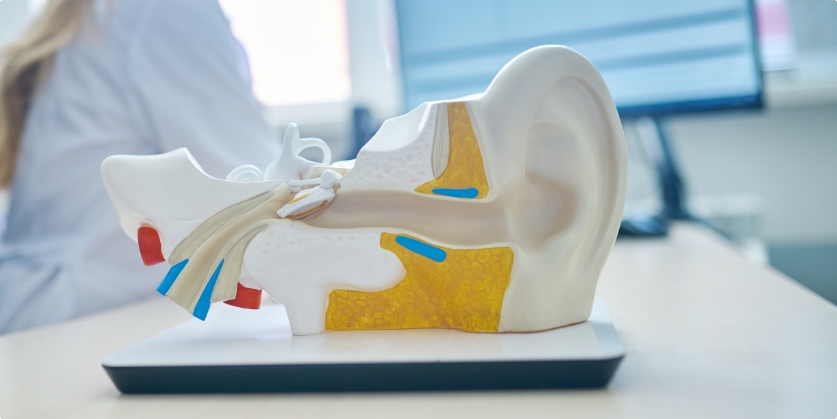
By Nobuko Ito, Au.D. Audiologist HearBright This is the story of a

By Nobuko Ito, Au.D. Board Certified Audiologist It was many years

By Nobuko Ito, Au.D., Audiologist HearBright, an Audiology Corporation Why